Any and All are two built ins provided in python used for successive And/Or.
Any
Returns true if any of the items is True. It returns False if empty or all are false. Any can be thought of as a sequence of OR operations on the provided iterables.
It short circuit the execution i.e. stop the execution as soon as the result is known.
Syntax : any(list of iterables)
# Since all are false, false is returned
print (any([False, False, False, False]))
# Here the method will short-circuit at the
# second item (True) and will return True.
print (any([False, True, False, False]))
# Here the method will short-circuit at the
# first (True) and will return True.
print (any([True, False, False, False]))
Output :
False
True
True
All
Returns true if all of the items are True (or if the iterable is empty). All can be thought of as a sequence of AND operations on the provided iterables. It also short circuit the execution i.e. stop the execution as soon as the result is known.
Syntax : all(list of iterables)
# Here all the iterables are True so all
# will return True and the same will be printed
print (all([True, True, True, True]))
# Here the method will short-circuit at the
# first item (False) and will return False.
print (all([False, True, True, False]))
# This statement will return False, as no
# True is found in the iterables
print (all([False, False, False]))
Output :
True
False
False
Practical Examples
# This code explains how can we
# use 'any' function on list
list_1 = []
list2 = []
# Index ranges from 1 to 10 to multiply
for i in range(1,11):
list_1.append(4*i)
# Index to access the list2 is from 0 to 9
for i in range(0,10):
list2.append(list_1[i]%5==0)
print('See whether at least one number is divisible by 5 in list 1=>')
print(any(list2))
Output:
See whether at least one number is divisible by 5 in list 1=>
True
# Illustration of 'all' function in python 3
# Take two lists
list_1=[]
list2=[]
# All numbers in list_1 are in form: 4*i-3
for i in range(1,21):
list_1.append(4*i-3)
# list2 stores info of odd numbers in list_1
for i in range(0,20):
list2.append(list_1[i]%2==1)
print('See whether all numbers in list_1 are odd =>')
print(all(list2))
Output:
See whether all numbers in list_1 are odd =>
True
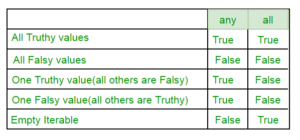
Truth table :-

No Comments