Classes and Objects are basic concepts of Object Oriented Programming which revolve around the real life entities.
Class
A class is a user defined blueprint or prototype from which objects are created. It represents the set of properties or methods that are common to all objects of one type. In general, class declarations can include these components, in order:
- Modifiers: A class can be public or has default access (Refer this for details).
- class keyword: class keyword is used to create a class.
- Class name: The name should begin with an initial letter (capitalized by convention).
- Superclass(if any): The name of the class’s parent (superclass), if any, preceded by the keyword extends. A class can only extend (subclass) one parent.
- Interfaces(if any): A comma-separated list of interfaces implemented by the class, if any, preceded by the keyword implements. A class can implement more than one interface.
- Body: The class body surrounded by braces, { }.
Constructors are used for initializing new objects. Fields are variables that provides the state of the class and its objects, and methods are used to implement the behavior of the class and its objects.
There are various types of classes that are used in real time applications such as nested classes, anonymous classes, lambda expressions.
Object
It is a basic unit of Object-Oriented Programming and represents the real life entities. A typical Java program creates many objects, which as you know, interact by invoking methods. An object consists of :
State: It is represented by attributes of an object. It also reflects the properties of an object.
Behavior: It is represented by methods of an object. It also reflects the response of an object with other objects.
Identity: It gives a unique name to an object and enables one object to interact with other objects.
Example of an object: person

Objects correspond to things found in the real world. For example, a graphics program may have objects such as “circle”, “square”, “menu”. An online shopping system might have objects such as “shopping cart”, “customer”, and “product”.
Declaring Objects (Also called instantiating a class)
When an object of a class is created, the class is said to be instantiated. All the instances share the attributes and the behavior of the class. But the values of those attributes, i.e. the state are unique for each object. A single class may have any number of instances.
Example:
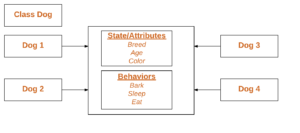
As we declare variables like (type name;). This notifies the compiler that we will use name to refer to data whose type is type. With a primitive variable, this declaration also reserves the proper amount of memory for the variable. So for reference variable, type must be strictly a concrete class name. In general, we can’t create objects of an abstract class or an interface.
Dog tommy;
If we declare reference variable(tommy) like this, its value will be undetermined(null) until an object is actually created and assigned to it. Simply declaring a reference variable does not create an object.
Initializing an object
The new operator instantiates a class by allocating memory for a new object and returning a reference to that memory. The new operator also invokes the class constructor.
// Class Declaration
public class Dog
{
// Instance Variables
String name;
String breed;
int age;
String color;
// Constructor Declaration of Class
public Dog(String name, String breed,
int age, String color)
{
this.name = name;
this.breed = breed;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
// method 1
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
// method 2
public String getBreed()
{
return breed;
}
// method 3
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
// method 4
public String getColor()
{
return color;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return("Hi my name is "+ this.getName()+
".nMy breed,age and color are " +
this.getBreed()+"," + this.getAge()+
","+ this.getColor());
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Dog tommy = new Dog("tommy","shih-Poo", 6, "white");
System.out.println(tommy.toString());
}
}
Output:
Hi my name is tommy.
My breed,age and color are shih-Poo,6,white
- This class contains a single constructor. We can recognize a constructor because its declaration uses the same name as the class and it has no return type.
- The Java compiler differentiates the constructors based on the number and the type of the arguments. The constructor in the Dog class takes four arguments.
- The following statement provides “tommy”,”shih-Poo”,6,”white” as values for those arguments:
Dog tommy = new Dog("tommy","shih-Poo",6, "white");
Note : All classes have at least one constructor. If a class does not explicitly declare any, the Java compiler automatically provides a no-argument constructor, also called the default constructor. This default constructor calls the class parent’s no-argument constructor (as it contain only one statement i.e super();), or the Object class constructor if the class has no other parent (as Object class is parent of all classes either directly or indirectly).
Ways to create object of a class
There are four ways to create objects in java.Strictly speaking there is only one way(by using new keyword),and the rest internally use new keyword.
- Using new keyword: It is the most common and general way to create object in java. Example:
// creating object of class Test
Test t = new Test();
Using Class.forName(String className) method: There is a pre-defined class in java.lang package with name Class. The forName(String className) method returns the Class object associated with the class with the given string name.We have to give the fully qualified name for a class. On calling new Instance() method on this Class object returns new instance of the class with the given string name.
// creating object of public class Test
// consider class Test present in com.p1 package
Test obj = (Test)Class.forName("com.p1.Test").newInstance(); - Using clone() method: clone() method is present in Object class. It creates and returns a copy of the object.
// creating object of class Test
Test t1 = new Test();
// creating clone of above object
Test t2 = (Test)t1.clone();
- Deserialization: De-serialization is technique of reading an object from the saved state in a file. Refer Serialization/De-Serialization in java
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(filename);
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(file);
Object obj = in.readObject();
Creating multiple objects by one type only (A good practice)
- In real-time, we need different objects of a class in different methods. Creating a number of references for storing them is not a good practice and therefore we declare a static reference variable and use it whenever required. In this case, wastage of memory is less. The objects that are not referenced anymore will be destroyed by Garbage Collector of java. Example:
Test test = new Test();
test = new Test();
- In inheritance system, we use parent class reference variable to store a sub-class object. In this case, we can switch into different subclass objects using same referenced variable. Example:
class Animal {}
class Dog extends Animal {}
class Cat extends Animal {}
public class Test
{
// using Dog object
Animal obj = new Dog();
// using Cat object
obj = new Cat();
}
Anonymous objects
Anonymous objects are the objects that are instantiated but are not stored in a reference variable.
- They are used for immediate method calling.
- They will be destroyed after method calling.
- They are widely used in different libraries. For example, in AWT libraries, they are used to perform some action on capturing an event(eg a key press).
- In the example below, when a key is button(referred by the btn) is pressed, we are simply creating anonymous object of EventHandler class for just calling handle method.
btn.setOnAction(new EventHandler()
{
public void handle(ActionEvent event)
{
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
});
